Cloud Computing Technology Assessment
Table Of Contents
Introduction
Definition of Cloud Computing
Cloud Computing Service Models
Cloud Computing Deployment Models
Why Cloud Computing?
Benefits and Drawbacks of Cloud Computing
Survey Results on Cloud Computing
Microsoft Office 365 and Windows Azure Cloud Model
Preface
By the word "Cloud" in technology term, we mean an online service through which we can get access to the contents as well as functionality any time and from anywhere. It is a real shift in computing mindset. The main shift is to move from "Software as a Product" concept to "Software as a Service" concept. Cloud computing is gaining popularity for its ease of access and worry free maintenance. But, there are lots of concerns about the Legal aspects of putting sensitive and confidential information into the grip of third party cloud service providers or online hackers. Industries are also thinking of TCO (Total Cost of Ownership), the Speed and Availability of online service applications etc.
Introduction
Cloud computing has gained immense popularity in the market. Ease of creating a full blown operational environment has made it very attractive. Getting access to the services from anywhere has added extra value to the new trend of cloud computing. There are still some legal challenges to put confidential information into the cloud.
Let us see what Cloud Computing is and why it is different than traditional computing. According to the definition of NIST, Cloud computing is a model for enabling convenient, on-demand network access to a shared pool of configurable computing resources (e.g., networks, servers, storage, applications, and services) that can be rapidly provisioned and released with minimal management effort or service provider interaction[i]. A Cloud Service provider will provide the virtual infrastructure or service into the cloud to quickly build and deploy applications without Purchasing any Hardware/Software, Maintaining or Upgrading the Infrastructure, overall getting access to the information anytime, anywhere and from any device.
Our aim is to find out details about Cloud Computing, Advantages and Disadvantages of Cloud Technology, Benefits of Cloud computing over the Traditional Computing, Cloud Computing Architecture and Cloud Service Providers.
Definition of Cloud Computing
The NIST definition is one of the clearest and most comprehensive definitions of cloud computing and is widely referenced in US government documents and projects. This definition describes cloud computing as having five essential characteristics, three service models, and four deployment models. The essential characteristics are:
- On-Demand Self-Service: Computing resources can be acquired and used at any time without the need for human interaction with cloud service providers. Computing resources include processing power, storage, virtual machines etc.
- Broad Network Access: The previously mentioned resources can be accessed over a network using heterogeneous devices such as laptops or mobiles phones.
- Resource Pooling: Cloud service providers pool their resources that are then shared by multiple users. This is referred to as multi-tenancy where for example a physical server may host several virtual machines belonging to different users.
- Rapid Elasticity: A user can quickly acquire more resources from the cloud by scaling out. They can scale back in by releasing those resources once they are no longer required.
- Measured Service: Resource usage is metered using appropriate metrics such monitoring storage usage, CPU hours, bandwidth usage etc.
Cloud Computing Service Models
Cloud Services are being offered based on different service models. There are various Could Service providers in the market of which Microsoft, VMWare, Amazon and Google are the ones to be mentioned. Cloud Service Offering and Pricing Model also varies from provider to provider.
Software as a Service (SaaS):
The capability for the customer to use the provider's applications running on the provider's cloud infrastructure. The applications are broadly accessible from an Internet browser. Although the customer does not manage any of the underlying infrastructure, the customer manages content and possibly some limited configuration settings.
This is where users simply make use of a web-browser to access software that others have developed and offer as a service over the web. At the SaaS level, users do not have control or access to the underlying infrastructure being used to host the software. Salesforce's Customer Relationship Management software and Google Docs are popular examples that use the SaaS model of cloud computing.
Platform as a Service (PaaS):
The capability for the customer to deploy application tiers, such as a database or a web service, to a container managed by the provider. The customer does not manage operating systems or infrastructure in this model, but has control over their application, data, and possibly some configuration settings.
This is where applications are developed using a set of programming languages and tools that are supported by the PaaS provider. PaaS provides users with a high level of abstraction that allows them to focus on developing their applications and not worry about the underlying infrastructure. Just like the SaaS model, users do not have control or access to the underlying infrastructure being used to host their applications at the PaaS level.
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS):
The capability to provision storage, archive, network, and server resources in a shared environment. Typically, server resources are deployed as virtual machines (VMs). The management of the server operating systems and other resources within this environment is performed by the customer, but the management of the underlying hardware and hypervisor is performed by the provider.
This is where users acquire computing resources such as processing power, memory and storage from an IaaS provider and use the resources to deploy and run their applications. In contrast to the PaaS model, the IaaS model is a low level of abstraction that allows users to access the underlying infrastructure through the use of virtual machines. IaaS gives users more flexibility than PaaS as it allows the user to deploy any software stack on top of the operating system. However, flexibility comes with a cost and users are responsible for updating and patching the operating system at the IaaS level.
Cloud Computing Deployment Models
Private Cloud: A Private Cloud being hosted within or outside and operated by the organization itself or by a Third Party provider but the use is exclusively by the same Organization.
Public Cloud: A Public Cloud is a common cloud for everyone. The Cloud service can be purchased based on Type of Service Models And / Or Number of Users and Type of Service being accessed. Public Clouds require significant investment and are usually owned by large corporations such as Microsoft, Google or Amazon.
Community Cloud: A Communality Cloud is generally shared by several organisations that shares the common goal.
Hybrid Cloud: Hybrid Cloud is the combination of Different Cloud Deployment models. In most cases, industries keep their confidential or corporate data in Private Cloud or On Premise environment and publish only the required information into the cloud.
Why Cloud Computing?
Vast majority of industries have taken initiatives to move partially/completely to Cloud or to look into the Cloud services from Cost, Maintenance, Availability and Performance point of view. Another big concern is, the Application providers are concentrating on Cloud as their platform of Service. Let's take a closer look at the Cloud predictions for the future[ii]:
More application availability on the cloud
Software product development companies are concentrating their effort on building Cloud based applications. Most of them are providing both solutions (Cloud and On-Premise) but most advanced features are being implemented in the Cloud Solution. Microsoft will release the new and advanced features into Office 265 before releasing it for SharePoint On-Premise server.
With most new software being built for cloud from the outset, it is predicted that by 2016 over a quarter of all applications (around 48 million) will be available on the cloud (Global Technology Outlook: Cloud 2014: A More Disruptive Phase).
Increased growth in the market for cloud
Based on their forecast for 2011-2017, Gartner expects adoption to hit $250 billion by 2017. In the same forecast, Gartner also suggested that the worldwide software as a service (SaaS) market would grow at an astounding yearly growth rate of 20.2 percent! This means it will be growing from $18.2 billion in 2012 to $45.6 billion in 2017.
More hybrid cloud adoption
By using Hybrid cloud structure industries can go into cloud into phases or separate out the sensitive or confidential/legal information and keep them into the corporate network whereas publish the rest of it into the Cloud. Gartner proposes that 50 percent of enterprises will have hybrid clouds by 2017. As we see more and more companies adopt cloud, we see CIOs crafting well-thought-out strategies that include cloud. However, pure cloud implementations are the exception and not the rule.
Increased development for the cloud
Software Product development companies started building products that is Cloud Based or compatible with certain cloud services. Cloud based developments are increasing significantly. According to Evans Data Corporation, there are more than 18 million software developers worldwide yet less than 25 percent are developing for the cloud today.
More innovation because of cloud
To make Cloud computing popular ad interactive, more innovations are coming into the Cloud Computing. As the Cloud based products are generally device independent, lots of innovations are coming to make cloud experience more interactive and attractive.
The Benefits of Cloud Computing
There are some significant benefits of Cloud Computing of which the following ones are the ones to be mentioned:
Flexibility
Cloud computing is highly flexible regarding the expansion of the operating environment. A cloud-based service can instantly meet the demand because of the vast capacity of the service's remote servers. Based on Salesforces' Information Week survey[iii], 65% of respondents said "the ability to quickly meet business demands" was an important reason to move to cloud computing.
High Availability
In Cloud environment, it is possible to add the servers into the availability group and service provider increases/decreases resources when required to make the Cloud environment Highly Available. Once the application is deployed, provisioning, load-balancing, health monitoring, are being handled by the cloud service provider. Based on SLAs the uptime of the applications are higher than On Premise deployments and may range up to 99.95% uptime in some cases.
Disaster recovery
In case of any disaster, the recovery is much faster in Cloud Computing. Cloud Service providers have online backup systems in place and being synced continuously.
Automatic software updates
Cloud Service Providers apply software updates automatically without disrupting the service. Customers don't have to think of applying software patches or software upgrades any more in Cloud Computing SaaS and PaaS models.
Auto Scalable and Upgradable
Cloud services are auto scalable. In case of more resources, it can be adjusted on the fly without affecting the application. But, the options may vary based on the service agreement for the subscribed services.
Application Development vs. Infrastructure Maintenance
Cloud solutions increases productivity by concentrating on the Actual development and delivery rather than spending much time on maintaining the System in terms of Hardware, Software, and Networks etc.
Convenient health monitoring and alerts
Cloud Service providers provide convenient health monitoring through Cloud dashboards or Alerts. It is very effective and free tool that is being used to identify any probable issue that will hamper the environment. Health and Monitoring is mostly part of the package for IaaS.
Cost Savings
Cloud Computing Cost Model is usage based and charged "pay-as-you-go". The cost model is a shift from Capital Expenses to Operating Cost and reduces total IT expenses. Maintenance and Support Costs are already included into the package. So, there is a big savings from the ma hours to maintain the infrastructure.
Increased collaboration
Cloud Computing increases collaboration between employees from different cities or countries. It keeps them all connected.
Any Device, Any Where
Cloud computing models support working from anywhere as long as employees have internet access. Most Cloud services are available from Any Device (i.e. iPad, iPhone, Windows Phone, Windows Tablets, and Android Phones/Tablets etc.). It increases productivity and supports "Bring Your Own Device" concept.
The Drawbacks of Cloud Computing
Security and Privacy
The information security and privacy are the major concerns over the cloud from user perspective. By leveraging a remote cloud based infrastructure, sensitive, confidential and legal information/documents are being hosted inside Cloud Service Provider's environment. In Multi-Tenant environment, the Data Center or Hosting Infrastructure is being shared by multiple companies. From the legal point of view some information/files cannot be kept outside of certain cities or countries. Keeping these aspects in mind, a careful decision has to be made.
Companies rely on Cloud Service providers to protect their data from un-authorized access or usages. Any un-authorized access could be a big threat for the company.
Performance
Depending on the type of application we deploy into Cloud Services, Performance factor may play a big role depending on which Data Centers we are connecting to and how much is the bandwidth is available from the Cloud Infrastructure.
Limited Control
Limited control is being provided for the deployment and administration of Cloud Services based for PaaS and SaaS deployment models. These deployment models lack of features compared to the Local Platforms or Applications.
Increased Vulnerability
Cloud based solutions are exposed to Internet and hence becomes more vulnerable target for malicious users and hackers. If security is being compromised, corporate data may be exposed to whole internet. This why strict security model need to be adopted and multi-factor authentication may be prescribed.
Technical Difficulties and Downtime
Cloud Computing is fully dependent on Stable Internet connections. If there is a problem in the internet, it may affect its whole purpose. Besides Internet, they could be some downtime or failure from Cloud service providers which may affect the entire company while accessing relevant information on time.
Survey Results on Cloud Computing
There have been lots of surveys done on Cloud Computing. I am going to share some of the survey results:
North Bridge Venture Partners (Mid 2014):
North Bridge Venture Partners, Gigaom Research and supported by more than 70 other collaborating organizations conducted the largest survey on Cloud Computing till Mid-Year of 2014[iv]. The survey analyzed the drivers and inhibitors behind cloud adoption, comparing the Cloud with Traditional technology with a sample of 1,358 respondents.
Cloud Adoption is Strategic
- 49% of respondents in this survey are using cloud to develop new products or applications
- 45% of businesses are already or planning to go to the Cloud
SaaS Adoption
- SaaS adoption increased from 11% (2011) to 74% (2014)
- Sales and Marketing adopted 51 %, whereas customer service and analytics both adopted at 43%.
IaaS and PaaS Adoption
- 56% of businesses are using Infrastructure-as-a-Service (IaaS)
- 41% of businesses are using PaaS technologies to prototype and develop new applications
- 2/3rd of respondents believe that their data will come to reside in some form of cloud over the next 2 years
Microsoft IT Pro Cloud Survey[v]
Microsoft conducted a survey on cloud computing. 1,979 people took part in this survey and the results are discussed below:
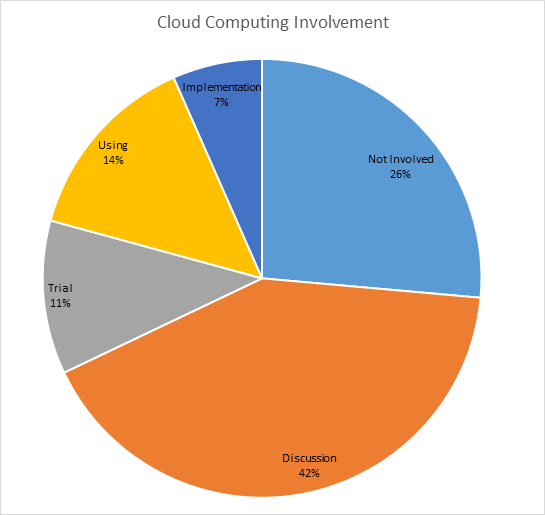
Cloud Computing Involvement:
Most important benefits of the cloud (Benefit from 1 to 5 with 1 being the most important):
Greatest Barrier in Cloud Computing:
Types of Cloud Computing:
Impact of cloud computing (Next 5 Years):
Knowledge of Cloud:
With cloud and hybrid services expected to reach US$108 billion by 2017[vi]. Microsoft also released their Cloud Service sales update brief of which is given below:
Microsoft Office 365:
- 77% of Fortune 500 companies have purchased it in the past 12 months
- With a US$2.5 billion run rate, it's Microsoft's fastest growing business
- Microsoft Office 365 posted triple-digit growth for 21 consecutive months
- Microsoft partners have accounted for 3/4 of the sales to Microsoft Office 365 customers
Microsoft Azure:
- 57% of Fortune 500 companies are using Microsoft Azure
- Welcomes 1,000 new customers per day Currently 1.2 million businesses and organizations use Microsoft Azure Active Directory
- Microsoft Azure gains two times the compute and storage capacity every 6-9 months
Microsoft Office 365 and Windows Azure Cloud Model[vii]
Microsoft's Cloud Platform named Windows Azure is well known in the Cloud Computing world. Amazon, Google, IBM are also proving cloud services at different levels of services. Microsoft Cloud provides added benefit by bringing Microsoft Office experience into the Cloud. Office 365 is Microsoft's Cloud product for SaaS (Software as a Service) and Windows Azure is the host platform for PaaS (Platform as a Service) and IaaS (Infrastructure as a Service) service offerings. Let us discuss details of Microsoft Cloud Service models.
SaaS (Software as a Service) – Office 365/CRM Online
Software as a Service (SaaS), meaning delivering software over the Internet -- provides the ability to simplify deployment and reduce acquisition costs. Microsoft Online Services are subscription-based, on-demand applications and hosted services, providing your organization with a consistent experience across multiple devices. Microsoft's SaaS model includes the following products:
- Microsoft Exchange Online delivers the email system in the Cloud. Businesses can migrate or host their email system into the Cloud without requiring any on premise infrastructure for Exchange.
- Microsoft SharePoint Online and Power BI provides the SharePoint Online for Collaboration and Content Management whereas Power BI for full blown Business Intelligence platform for the enterprise.
- Microsoft Office Professional Plus is available in select Microsoft Office 365 service plans and provides Microsoft Office through web browsers and from any device without practically having Microsoft Office installed into the machine.
- Microsoft Lync Online provides the online communication platform for the business. Employees can communicate through Voice, Video Conferencing, and Texting/Chatting through Online presence
- Microsoft Dynamics CRM Online delivers rich sales automation, service management, and marketing automation functionality through the browser and within everyday productivity applications of the business
Office 365 includes Exchange, SharePoint, and Office Professional plus as a part of their combined SaaS cloud offering whereas Dynamics CRM and Power BI are offered as a part of different service model.
PaaS (Platform as a Service) - Windows Azure
PaaS stands for Platform as a Service. In this mode, it's possible to deploy and run customized applications/services with limited control. The basic infrastructure, network topology, load balancers are all configured automatically. Windows Azure PaaS provides with data services, including a relational database, reporting and data synchronization. Both Windows Azure and SQL Azure are the key components of the Azure Cloud Platform. It is easy to scale up or scale down SQL server according to the application need. One of the key benefits of PaaS is that we don't have to be concerned about the Operating System, Platform Features, Upgrade or Maintenance.
IaaS (Infrastructure as a Service) - Windows Azure
In IaaS model, full infrastructure can be outsourced to the Cloud including Virtual Servers, Storage, Networking, Load Balancers ad so on. The full infrastructure or network can be accessed through secured internet. In SaaS model, it's the subscribed business's responsibility to maintain the Infrastructure including Patches/Updates or regular monitoring. Azure IaaS is pretty much same as office infrastructure except it is in the Cloud. IaaS subscription model depends on computing power that Business is using (No. of Cores, memory, HDD, network, bandwidth etc.). But, the easy part is to provisioning a new server. New server can be built based on existing server templates (LINUX, UNIX, Windows, SharePoint etc.) within 5-10 minutes. IaaS provides granular control to the infrastructure and additional resources can be added, upgraded or removed from Virtual Machine management console.
Hybrid Cloud Architecture
Hybrid Cloud is the combination of different Cloud Deployment models. A hybrid cloud is the combination of at least one public and one private cloud, with the workload distributed across the two. In most cases, industries keep their corporate data in the Private Cloud or On Premise environment and publish only the required information into the Public cloud.
In Hybrid Cloud environment, we have to segregate the applications and services between On Premise/Private Cloud and Public Cloud. In some cases, we may have to extend the existing applications from Premise/Private Cloud to Public Cloud. While extending applications and services into another cloud is determining how to ensure that access to these services is consistent for the users. So, we have to get the answers of the following questions before approaching Hybrid Cloud platform:
· Will services deployed in the public cloud run directly on the Internet?
· How will you manage identity for internet-facing services?
· Do those services require access to systems and data in the private cloud?
If we need the services to connect to the Private Cloud or On Premise databases/applications, careful consideration needs to be made about how to connect these services while protecting corporate/sensitive data and networks. A public cloud like Azure offers many different ways to connect these services. It also offers Windows Azure Service Bus for secured and scalable way to communicate between services through internet-standard protocols. But, the traditional option is also available to communicate through secured VPN tunnels. For large scale deployments, Microsoft is investing in high-speed interconnect options like MPLS connections to Azure with some cell carriers. Hybrid cloud can be separated by web service layers or consumable service API's from Public Cloud. Hybrid applications can be designed by adopting IT policy, SLAs, Security, and Data Sovereignty. SLA will dictate application will be placed in Private or Public Cloud. Based on Data Security policy and legal implications data store can be inside corporate network whereas the application could be in the Public.









William Hill Sign Up Offer » Get the best welcome bonuses
ReplyDeleteWilliam Hill Sportsbook App — Our review of the William Hill Sportsbook's bonus code and the sign-up offer. Claim your bonus with jeetwin William Hill and william hill enjoy William Hill Promo Code: Just click hereWilliam Hill Casino Bonus: £50 Welcome BonusWilliam Hill m88 Mobile App: Great for new customersWilliam Hill Mobile Deposit Methods: Skrill & credit cardWilliam Hill Sportsbook Promo Code: Click Here